Cisco 881G - Configuring Dynamic Failover On a Backup 3G Cellular Link
09 Jan 2012My latest lab toy is a Cisco 881G which integrates a cellular 3G interface used a secondary data link. In the following article I will present the existing scenario and what needs to be acomplished.
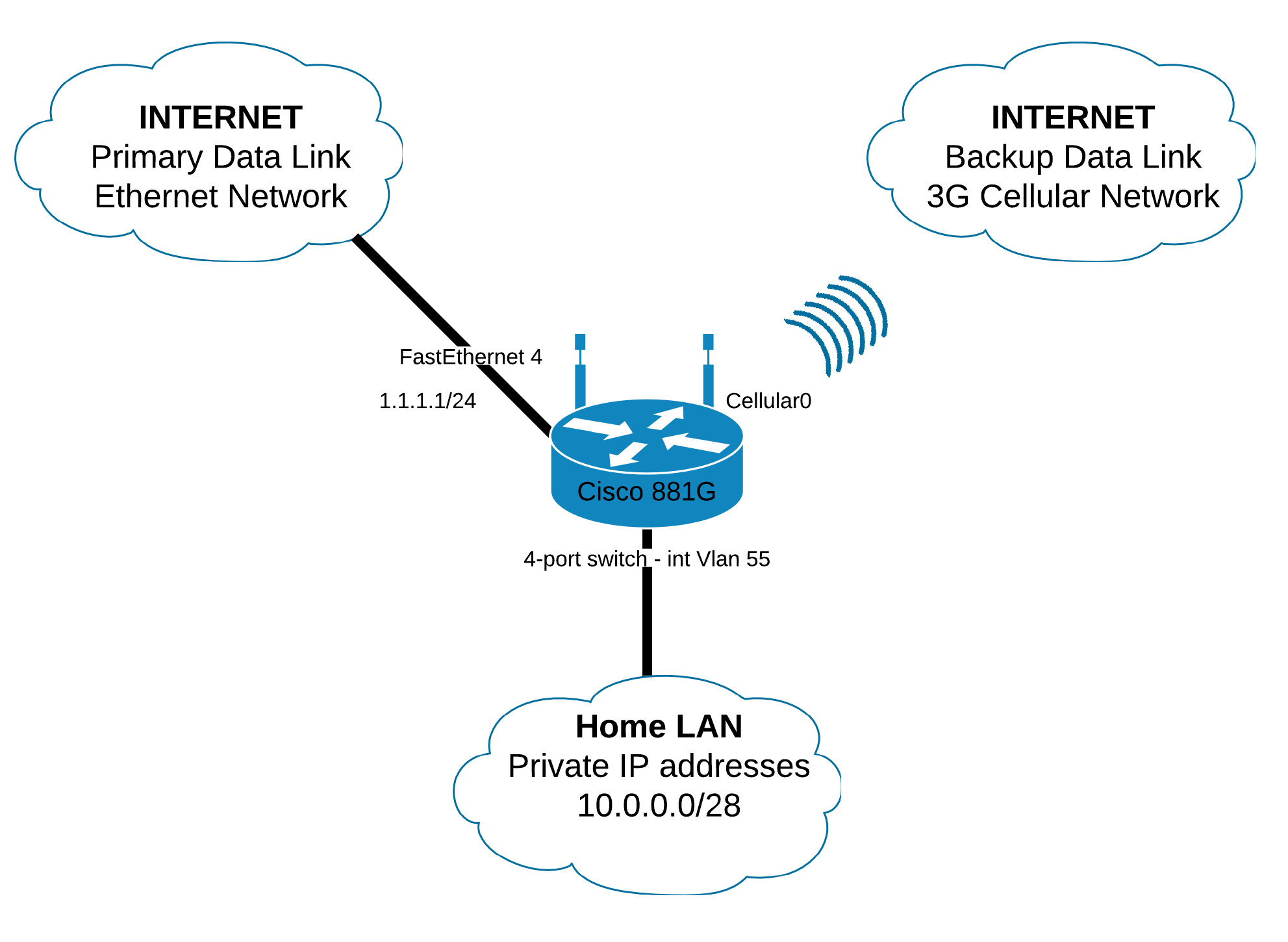
What’s the scenario? We have a small LAN using private IP addresses which need to be translated on both the external links. The primary link is an Ethernet drop so it’s very unlikely to change its state to down so that the router can detect the link failure and make the changes in its RIB. In order to detect a failure on the primary link we have to implement a mechanism which takes an external point as reference and measures different parameters. For instance in my scenario we will send ICMP packets to an external IP address - 8.8.8.8, the Google public DNS server, and measure the RTT. As long as the RTT value is within certain limits the default route will be set on the primary link. If it exceeds that value then the default route set on the primary link will be dropped out of the routing table and a secondary default route - the one from the backup link, which has a higher administrative distance will take its place.
We have to make sure that the ICMP packets sent for checking the RTT will be sent only from the primary link. Otherwise when the backup link becomes active it checks the RTT and gets a proper value and it install the primary default route thus resulting in a loop of default routes.
Enough with the words, now let’s get to the config lines:
First of all, let’s configure the cellular interface so that it can connect to the 3G network:
Configuring the cellular interface
We must ensure that the SIM card is not locked with a PIN code - Cellular 0 is the interface:
Router#cellular 0 gsm sim unlock $PINWe need to create a gsm profile with the settings associated with your data account:
Router#cellular 0 gsm profile create 1 internet ipv4 pap cisco cisco
"1" - Profile number
"internet" - Access Point Name
"ipv4" - Packet Data Protocol
"pap" - Authentication type
"cisco" - Username
"cisco" - PasswordNext we need to create a chat script which sends commands to the 3G modem to connect to the remote system. The chat script is called CellScript with a timeout value of 30 seconds. Please note that the script may be different depending on the carrier.
Router(config)#chat-script CellScript "" "ATDT*98*1#" TIMEOUT 30 "CONNECT"
"1" - represents the number of the gsm profile created aboveAssociate the created chat script to the 3G modem line, for the 881G is line 3:
Router(config)#line 3
Router(config-line)#script dialer CellScriptNext we should create a Dialer interface:
Router(config)#interface Dialer2
Router(config-if)#ip address negotiated
Router(config-if)#ip virtual-reassembly in
Router(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
Router(config-if)#dialer pool 2
Router(config-if)#dialer idle-timeout 0
Router(config-if)#dialer string CellScript
Router(config-if)#dialer persistent
Router(config-if)#dialer-group 2
Router(config-if)#ppp authentication pap callin
Router(config-if)#ppp pap password 7 045F1E0B0238
Router(config-if)#ppp ipcp dns request
Router(config-if)#no cdp enableThe next step required is to configure the Cellular interface
Router(config)#interface Cellular0
Router(config-if)#ip address negotiated
Router(config-if)#ip virtual-reassembly in
Router(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
Router(config-if)#dialer in-band
Router(config-if)#dialer pool-member 2
Router(config-if)#dialer idle-timeout 0
Router(config-if)#dialer-group 2
Router(config-if)#async mode interactiveCreate a dialer list which allows IP packets for the interfaces in dialer group 2:
Router(config)#dialer-list 2 protocol ip permitAdd a default route and you should have a working 3G data link:
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer2Configuring NAT with multiple pools
OK, now that we have set the 3G backup data link I assume that you know how to configure the primary Ethernet link so we can pass to the next section: how to get Network Address Translation work on both interfaces. First we need to set an access list which identifies our private addresses - in my case: 10.0.0.0/28
Router(config)#access-list 10 permit 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.15Next we’ll create route maps which identify both the private ip addresses by the ACL created above and the external interface:
Router(config)#route-map PRIMARY permit 1 ; 1 is a sequence number in the route map function
Router(config-route-map) #match ip address 10 ; matches all IP traffic identified by ACL 10
Router(config-route-map)#match interface FastEthernet4
Router(config)#route-map BACKUP permit 1
Router(config-route-map) #match ip address 10
Router(config-route-map)#match interface Dialer2Last we have to set the NAT direction on the interfaces we are interested in:
Router(config)#interface Vlan 55
Router(config-if)#ip nat inside
Router(config)#interface FastEthernet4
Router(config-if)#ip nat outside
Router(config)#interface Dialer2
Router(config-if)#ip nat outsideNow that we have the route maps set we need the create the NAT translation rules. On both of the interfaces I will set NAT overload as I have a single IP address assigned by the ISP:
Router(config)# ip nat inside source route-map PRIMARY interface FastEthernet4 overload
Router(config)# ip nat inside source route-map BACKUP interface Dialer2 overloadConfiguring dynamic failover with Cisco IP SLAs
The address translation is complete too. In the next section we will implement the dynamic failover mechanism using Cisco IP Service Level Agreements ( SLAs ). The Cisco IOS IP SLA is a powerful tool which can help improve your networks services. It allows you to monitor traffic parameters like round-trip delay, one-way delay, one-way jitter, packet loss, TCP connection time, DNS lookup time and many others. Let’s get to the config line and show how we should implement the SLAs.
Router(config)#ip sla 1
Router(config)#icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 interface FastEthernet 4 ; pings 8.8.8.8 with the source address of Fa4
Router(config)#timeout 150 ; the amount of time in milliseconds the IP SLA operation waits a response from its request packet
Router(config)#frequency 2 ; the amount of time in seconds at which the IP SLA operation performs
Router(config)#ip sla schedule 1 life forever start-time nowTo review the above config lines: The routers pings 8.8.8.8 with ICMP REQUEST packets having the source address of Fa4 and if an ICMP REPLY packet isn’t received within 150ms the IP SLA operation is considered to have failed. This process is repeated once every 2 seconds. We set this process to start now and occur forever.
Now what happens if the IP SLA operation fails? In the following lines we’ll tell the router what to do in that case:
We need to create a track object to monitor the status of the IP SLA we have created:
Router(config)#track 1 ip sla 1 reachabilityThe track object informs the static route if a state change of the IP SLA occurs.
Next we will associate the primary default route with the tracker.
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet4 track 1and assign a higher administrative distance to the secondary default route:
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer2 10And that should be all. You should now have a dynamic failover route without having to enable dynamic routing protocols. Pretty cool :)