Upgrading Openstack from Newton to Ocata with TripleO
14 May 2017During the last cycle I’ve been working on testing upgrades from Newton to Ocata and in this post I’ll describe how the upgrade process looks like and share some tips which might be helpful when you’re upgrading.
Deployment
We’re going to start with a composable roles RDO deployment including:
- 3 x controller nodes running the control plane services
- 2 x networker nodes running Neutron agents
- 3 x cephstorage nodes running Ceph OSDs
- 2 x compute + 2 x computealt nodes running Nova compute
We have 2 types of heterogeneous hardware used for the compute hypervisors so we split them into different roles in order to be able to apply per role configurations.
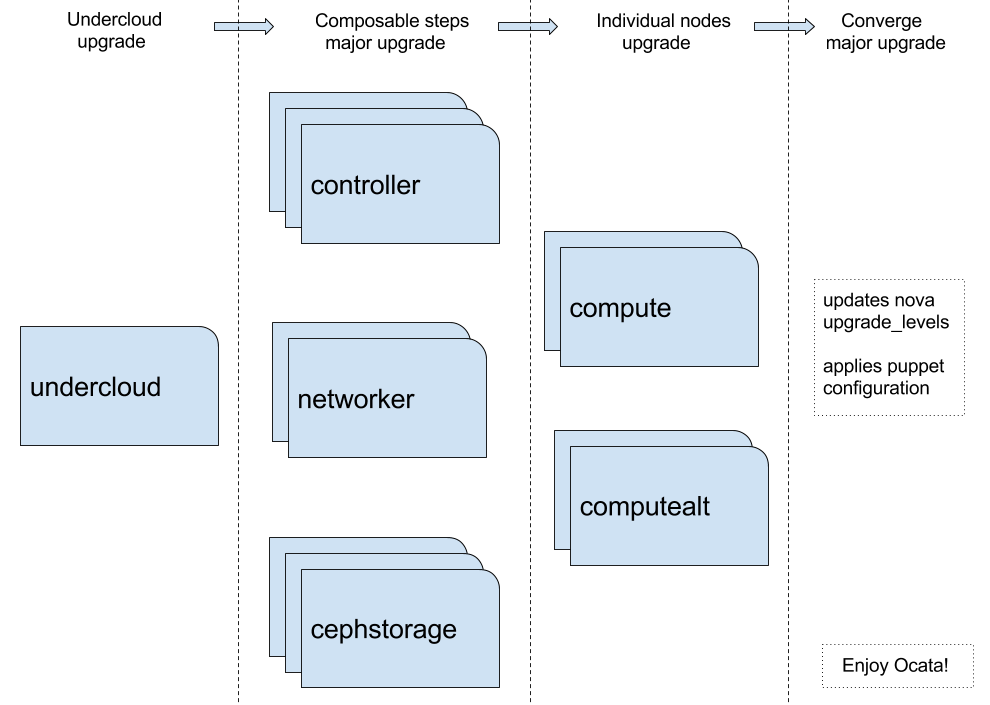
Upgrade
I’m going to describe below the overall upgrade steps and later we’ll go through the details and commands that are required for implementation.
The upgrade process consists of the following main stages:
-
Undercloud upgrade
-
Composable steps major upgrade
In Ocata the concept of composable upgrades was introduced. This means that each service has assigned a set of Ansible tasks which get run during upgrade. Each of these tasks is tagged with a step that signifies when it gets run.
From a high level perspective during upgrade we first stop the services, then upgrade(including service specific steps) and then bring the services back on. For now only the Ceph services support rolling upgrades(one node at a time). This means that we should expect to see control plane downtime while performing these steps. Nevertheless we expect the data plane not to be affected so instances availability should not be interrupted.
During this phase we have the ability to disable upgrades for services running on specific roles. By default upgrade is disabled for compute and swift object storage roles to allow the user to do maintenance related activities while upgrading individual nodes such as migrating instances before upgrade, rebooting nodes post upgrade, etc.
-
Individual nodes upgrade
Nodes part of the roles that are not upgraded during the composable steps can be individually upgraded by using the upgrade-non-controller.sh script.
-
Upgrade converge
During converge step we unpin Nova RPC version and the puppet configuration gets reapplied on all overcloud nodes.
Undercloud upgrade
- Disable Newton repos
sudo yum-config-manager --disable '*newton*'- Enable Ocata repos
sudo yum install -y centos-release-openstack-ocata- Stop services before upgrade
sudo systemctl stop openstack-* neutron-* httpd- Upgrade packages before upgrade
sudo yum -y update instack-undercloud openstack-puppet-modules openstack-tripleo-common python-tripleoclient- Upgrade undercloud
openstack undercloud upgradeAt this point the undercloud is upgraded and running Ocata.
Overcloud upgrade
Switch repos
- Disable Newton repos
source ~/stackrc
for node in $(nova list | awk '{print $12}' | grep -oP '[0-9.]+'); do ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -l heat-admin $node 'sudo yum-config-manager --disable '*newton*'';done- Enable Ocata repos
source ~/stackrc
for node in $(nova list | awk '{print $12}' | grep -oP '[0-9.]+'); do ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -l heat-admin $node 'sudo yum install -y centos-release-openstack-ocata';doneUpdate roles_data.yaml
Services adjustments:
In Ocata some of the services in roles_data.yaml were deprecated and new ones were introduced. In our case, since we’re using a custom role_data.yaml, we need to manually adjust it to include these changes.
The following services were removed so they need to be removed from roles_data.yaml
OS::TripleO::Services::Core
OS::TripleO::Services::GlanceRegistry
OS::TripleO::Services::VipHostsThe following services were newly introduced and are active by default so they need to be added to roles_data.yaml
OS::TripleO::Services::MySQLClient
OS::TripleO::Services::NovaPlacement
OS::TripleO::Services::PankoApiIn addition there are new services which are not activated by default so they’re not mandatory. I recommend checking the complete list of services in the tripleo-heat-templates roles_data.yaml
Disable roles upgrade:
While at this step we also want to mark the roles where we want to upgrade individual nodes, in our case the compute nodes. Skipping upgrade for these roles is done via the disable_upgrade_deployment flag and since we have 2 type of compute roles we want to assign this flag to both of them:
- name: Compute
disable_upgrade_deployment: True
[...]
- name: ComputeAlt
disable_upgrade_deployment: True
[...]Composable steps major upgrade
Run the major upgrade composable steps by adding the major-upgrade-composable-steps.yaml Heat environment file to the openstack overcloud deploy command used for the initial deployment:
source ~/stackrc
export THT=/usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/
openstack overcloud deploy --templates $THT \
-r ~/deployment/roles/roles_data.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/puppet-pacemaker.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/network-isolation.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/network-management.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/storage-environment.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/nodes.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/network-environment.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/disk-layout.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/neutron-settings.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/major-upgrade-composable-steps.yaml During this step services running on all the roles except the ones which were specifically disabled in roles_data are being upgraded.
Individual nodes upgrade
Individual nodes can be upgraded via the upgrade-non-controller.sh script:
source ~/stackrc
upgrade-non-controller.sh --upgrade overcloud-compute-0Before upgrading a compute node one might consider to migrate the workloads to another node in order to avoid potential issues which may arise during the upgrade. A reboot is also required in case components such as the kernel or openvswitch get upgraded so once the upgrade is finished it is a proper time for reboot.
Commands that I found useful while migrating workloads:
## migrate all instances from specific host
nova host-evacuate-live
## migrate specific instance to specific host
nova live-migration The openstack unified CLI can output in JSON format which is easy to parse with the help of jq:
openstack server list -f json | jq -r -c '[.[] | select(.Status | contains("ACTIVE") or contains("PAUSED")) | .Name]'
## outputs instances which are in ACTIVE or PAUSED stateConverge major upgrade
Once all the compute nodes have been upgraded we can move forward to the last step in the upgrade process. During previous steps the upgrade_levels configuration section contained ‘compute = auto’ in nova.conf. The converge step removes this option and reapplies the puppet configuration on all overcloud nodes.
source ~/stackrc
export THT=/usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/
openstack overcloud deploy --templates $THT \
-r ~/deployment/roles/roles_data.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/puppet-pacemaker.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/network-isolation.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/network-management.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/storage-environment.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/nodes.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/network-environment.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/disk-layout.yaml \
-e ~/deployment/environments/neutron-settings.yaml \
-e $THT/environments/major-upgrade-converge.yamlAt this point the upgrade process is complete and both undercloud and overcloud are running Ocata.
Upload new overcloud images
As one last step we want to update the overcloud images so new nodes which are going to be added later to the deployment load the current version images and not the old ones. To do this we should to go to the directory where images have been built/downloaded and run:
## Download images from https://images.rdoproject.org/
source ~/stackrc
openstack overcloud image upload --update-existingPost upgrade actions
Some of the upgraded software components (e.g kernel, openvswitch) require a node reboot to get their new versions loaded. We’re going to take this step to reboot the remaining nodes in the deployment. All the nodes are deployed in an HA topology so we can reboot them one by one so the service availability doesn’t get affected.
We’ll start with the Ceph OSD storage nodes. Before rebooting a node we want to set noout and norebalance flags for the OSDs to avoid rebalancing. Once the node is rebooted we unset the flags, make sure that the cluster is in a HEALTH_OK state and move to the next node in the cluster.
Commands that I found useful while rebooting the Ceph OSD nodes:
## set the flags to avoid rebalancing
ceph osd set noout
ceph osd set norebalance
## make sure all pgs are active+clean
ceph pg stat
## unset flags
ceph osd unset noout
ceph osd unset norebalance
## make sure cluster is in HEALTH_OK
ceph healthGoing forward to the networker nodes we can reboot them in a rolling fashion, waiting for the node and its Neutron agents respectively to come back online and then move to the next one. Floating IPs failover will automatically occur when the agent goes down.
Commands that I found useful while rebooting the Networker nodes:
## list all neutron agents
neutron agent-list
## list neutron routers
neutron router-list
## list dhcp agents assigned to particular net
neutron dhcp-agent-list-hosting-net
## list l3 agents assinged to particular router
neutron l3-agent-list-hosting-routerIn the last step we’re going to reboot the controller nodes serially, waiting for each node to come back online in the pacemaker cluster and verifying that all pacemaker resources, haproxy backends and Openstack systemd services are running.
Commands that I found useful while rebooting the Controller nodes:
## pacemaker cluster status
pcs status
## get haproxy stats
echo show stat | nc -U /var/lib/haproxy/stats
## show openstack systemd services
systemctl list-units openstack-*